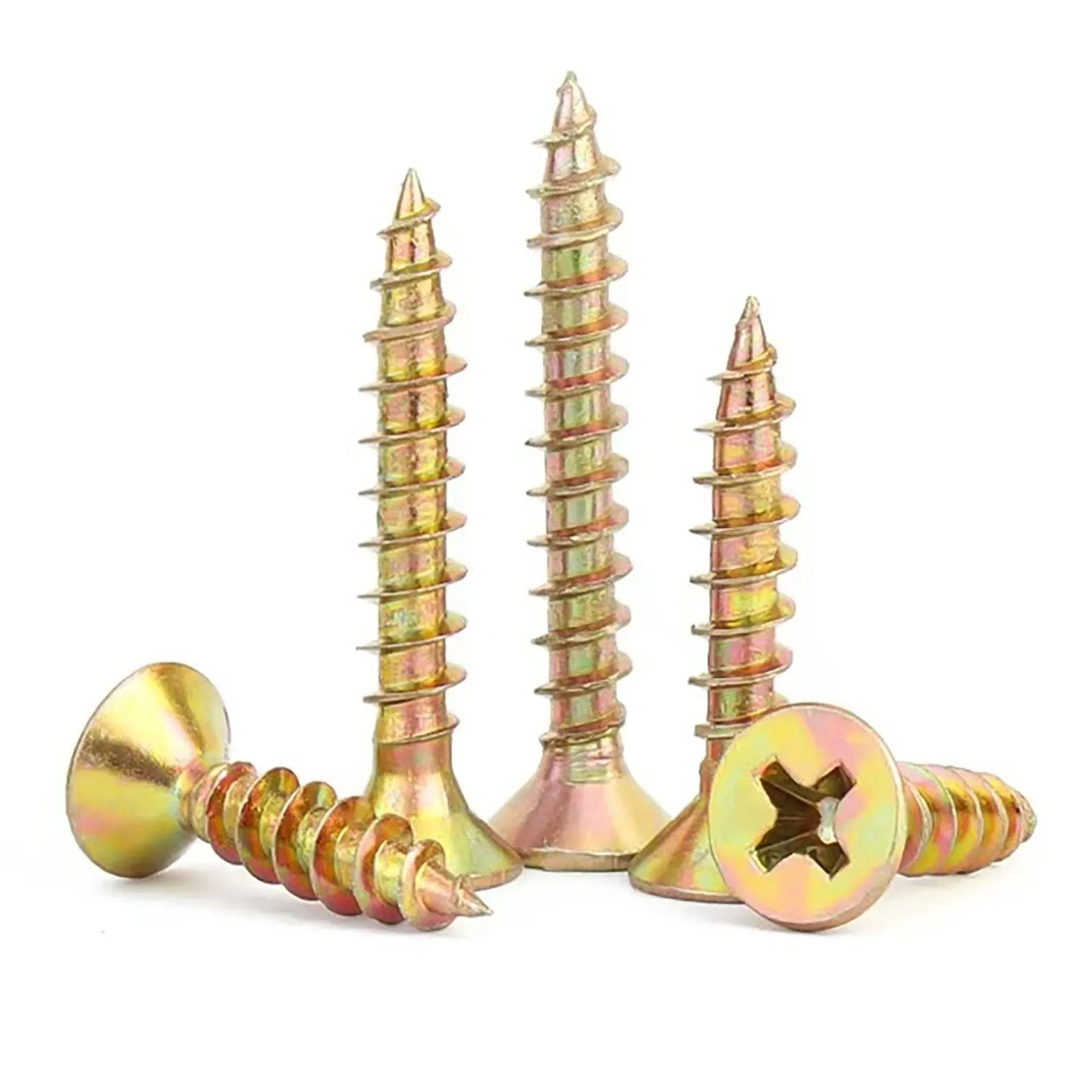
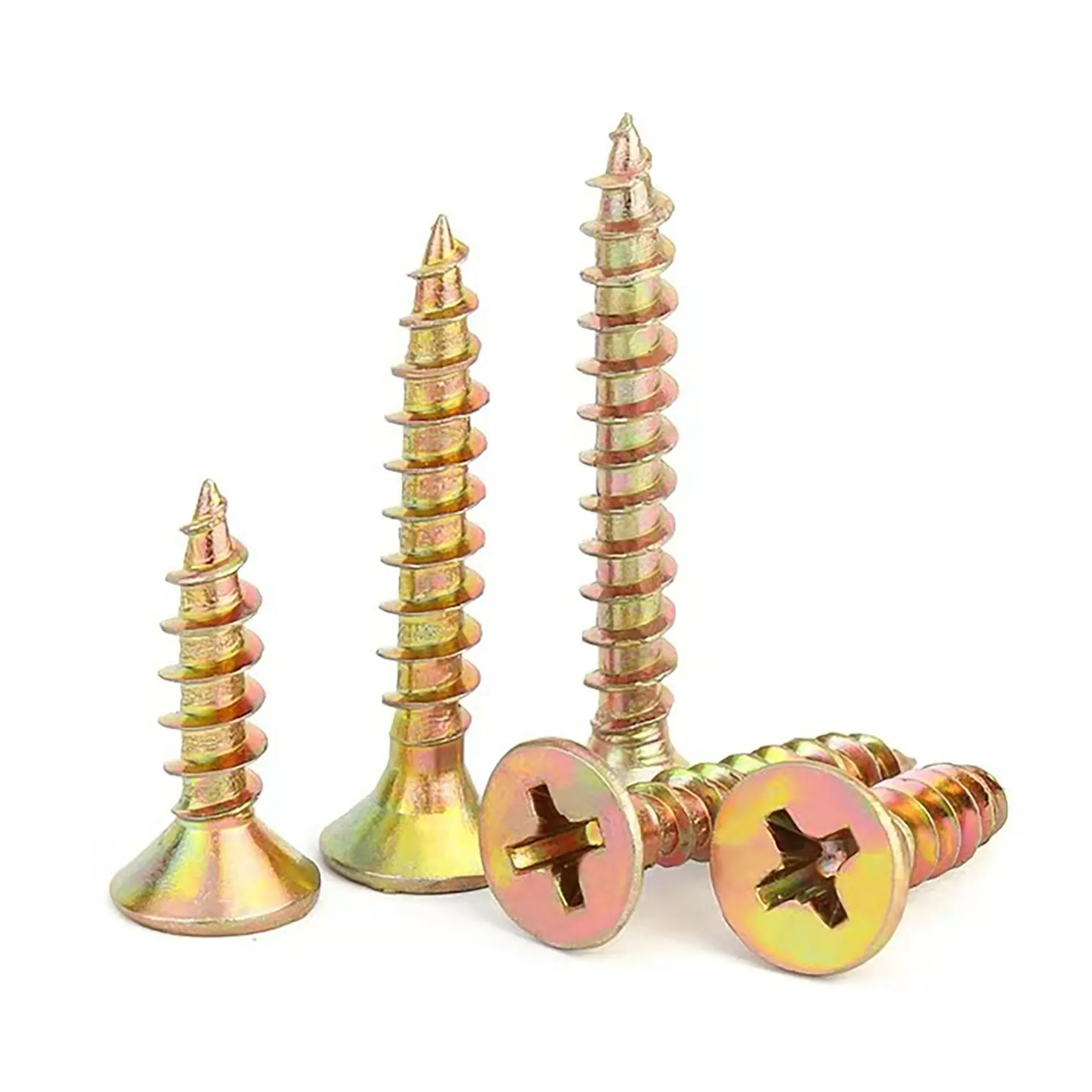
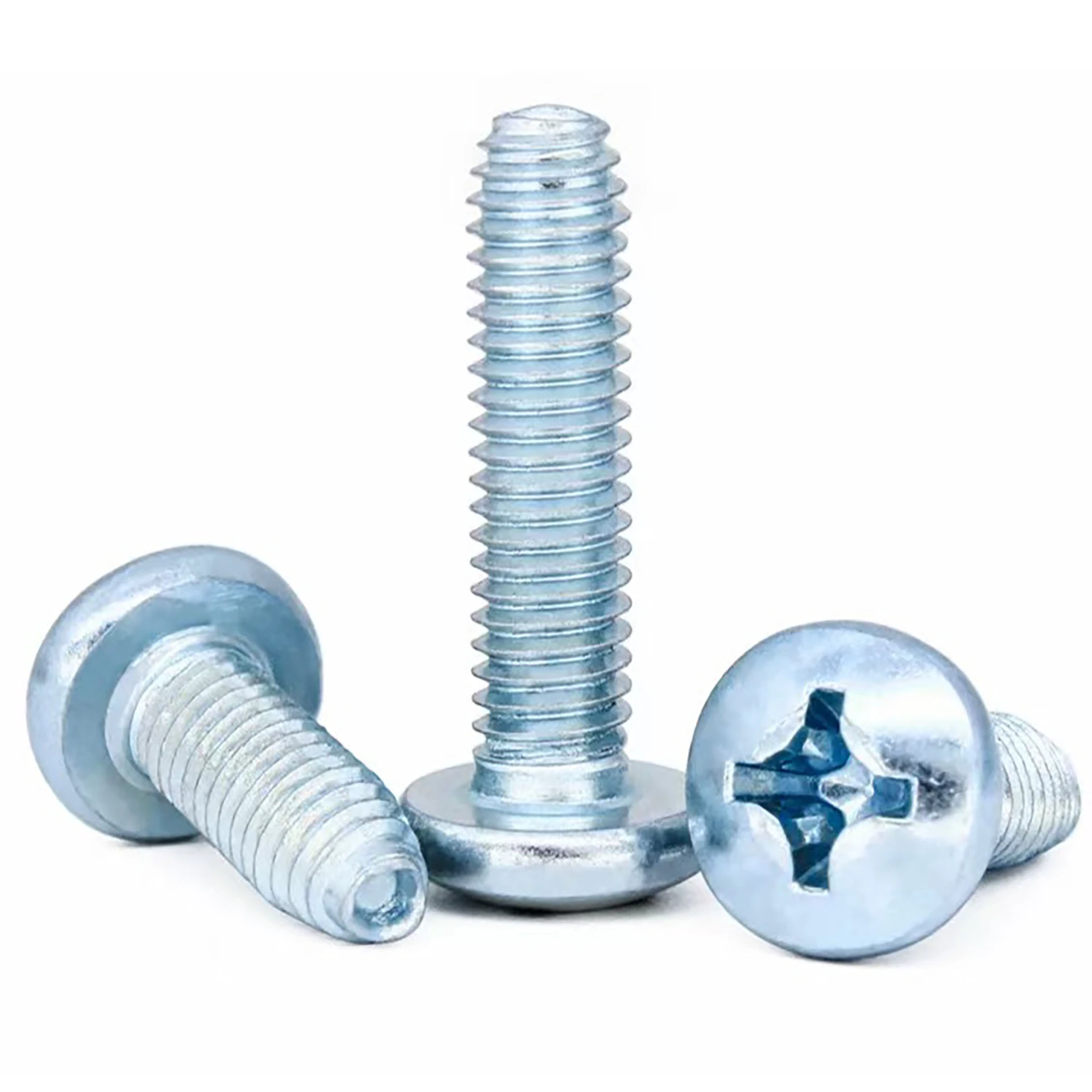
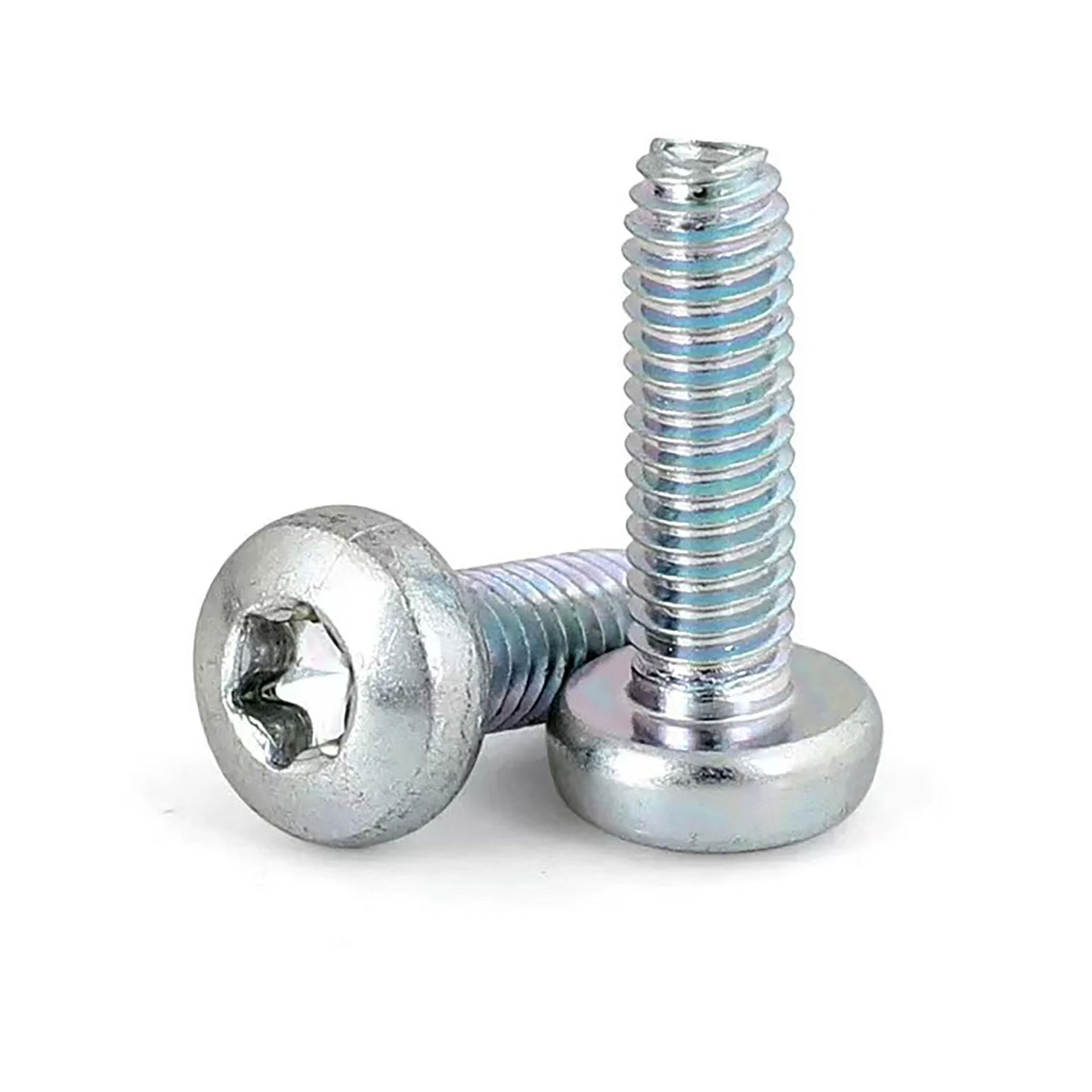
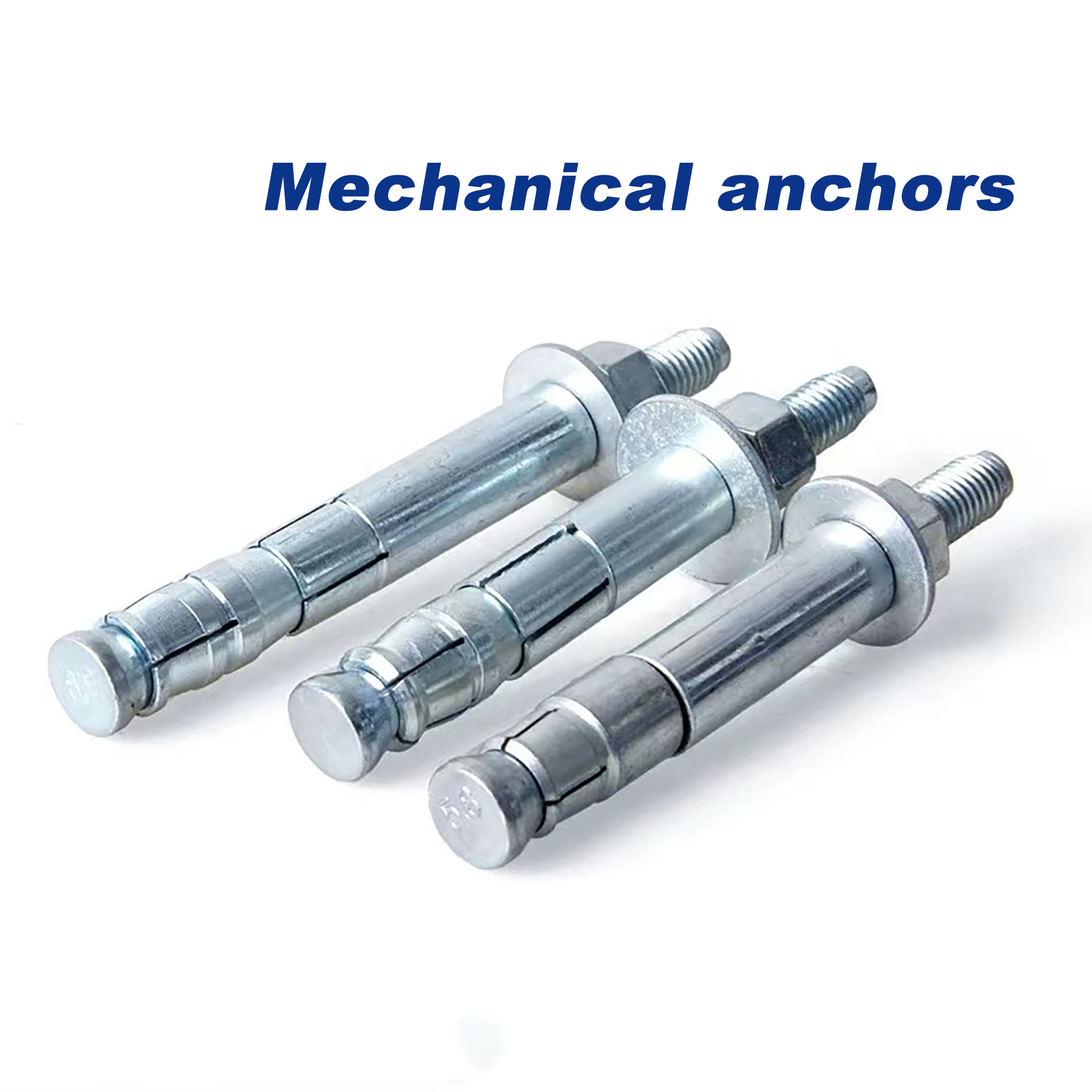
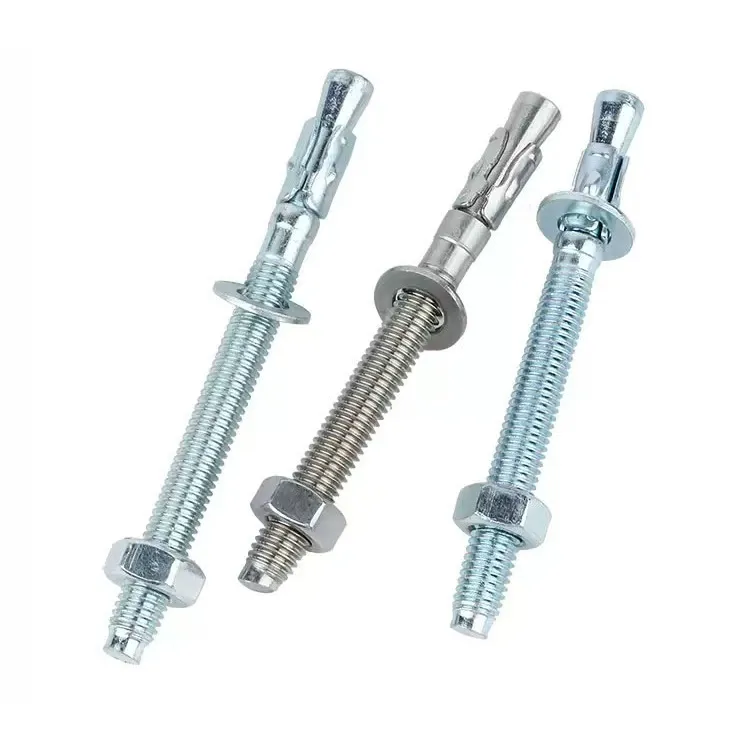
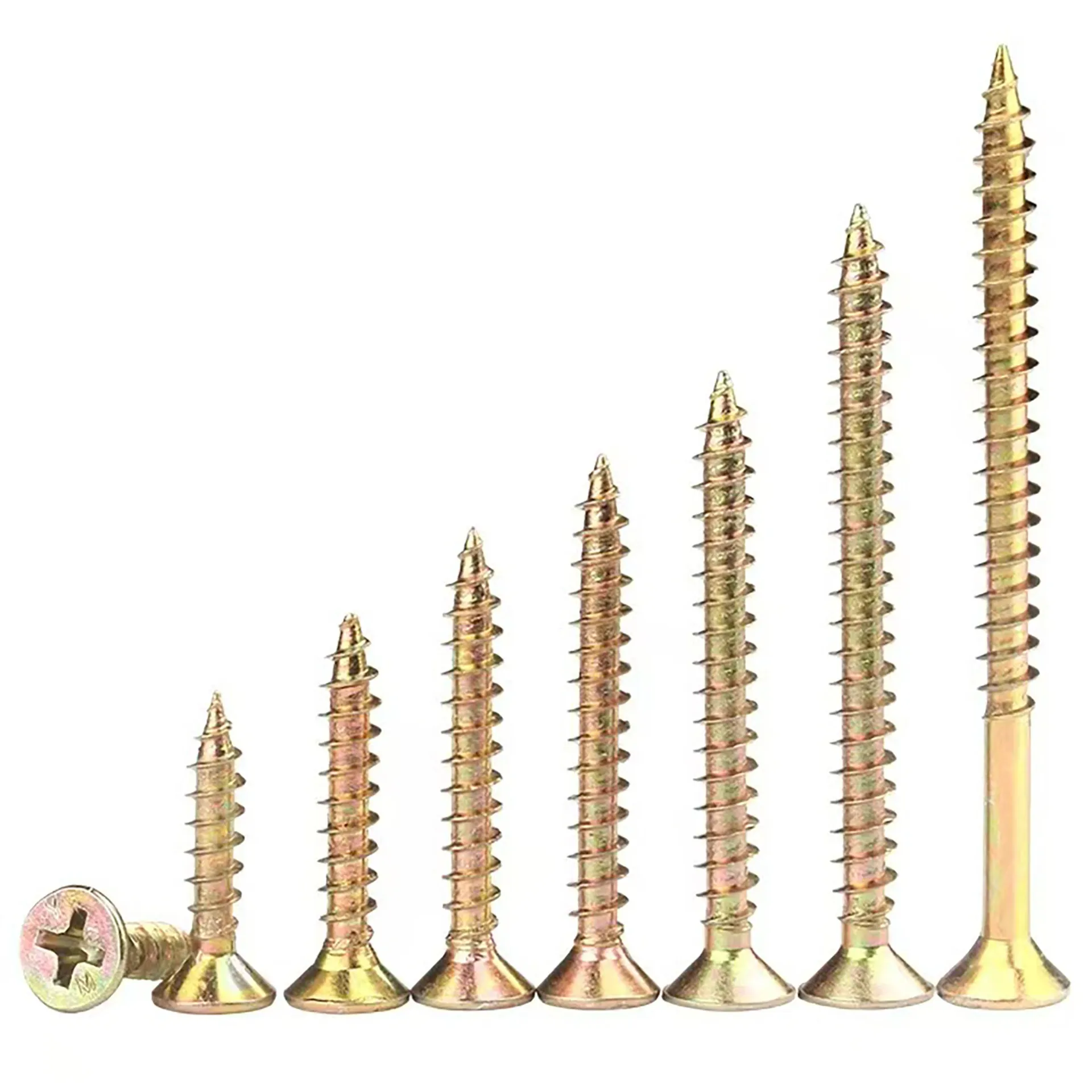
Pan Head Phillips Self-Drilling Screws
The Pan Head Phillips Self-Tapping Screw is a standard fastener widely used for joining thin metal sheets, plastics, wood, and composite materials. Its defining feature is that no pre-tapping (threading after drilling) is required. Utilizing its specially designed threads, it cuts or forms matching internal threads directly into softer materials during installation, enabling fast and efficient connections. The pan head design provides a large bearing surface and facilitates manual tool operation, while the Phillips drive is the most common screwdriver interface.

Core Features & Advantages
Self-Tapping Functionality:
No Pre-Tapping Needed: Eliminates the step of tapping internal threads after drilling, simplifying installation, significantly improving assembly efficiency, and reducing labor and time costs.
Thread-Forming or Thread-Cutting: Features a sharp thread point designed to cut into materials (like wood, plastic) or form threads by displacement in softer metals (like thin steel or aluminum sheets).
Process Efficiency: Particularly suited for mass production and on-site installation.
Pan Head Design:
Large Bearing Surface: The relatively large head diameter provides greater contact area, effectively distributing clamping pressure and minimizing surface damage or sinking into softer materials.
Ease of Manual Operation: Moderate head height allows for stable application of force with screwdrivers or power tools.
Aesthetic Appeal: Rounded head profile offers a relatively neat appearance after installation.
Phillips Drive:
High Versatility: Phillips screwdrivers and bits are the most ubiquitous and easily accessible tools.
Centering Aid: Helps maintain driver centering during initial engagement.
Torque Transmission: Designed to transmit moderate torque. Features "cam-out" (driver slippage) at a preset torque limit to prevent over-tightening, which could damage the screw head or fracture the material (requires using appropriate tools and torque settings).
Materials & Finishes:
Common Materials: Carbon steel (enhanced by finishes), Stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316 for corrosion resistance), Brass (conductive, corrosion resistant), Aluminum alloy (lightweight).
Common Finishes:
Zinc Plating (Blue/White, Yellow): Cost-effective, provides basic rust resistance.
Nickel Plating: Bright silver appearance, better corrosion resistance than standard zinc plating.
Dacromet/Zinc Flake Coating: Provides very high corrosion resistance, ideal for harsh environments.
Black Oxide/Phosphating: Offers basic rust resistance and friction reduction.
Plain (Stainless Steel): Relies on material's inherent corrosion resistance.
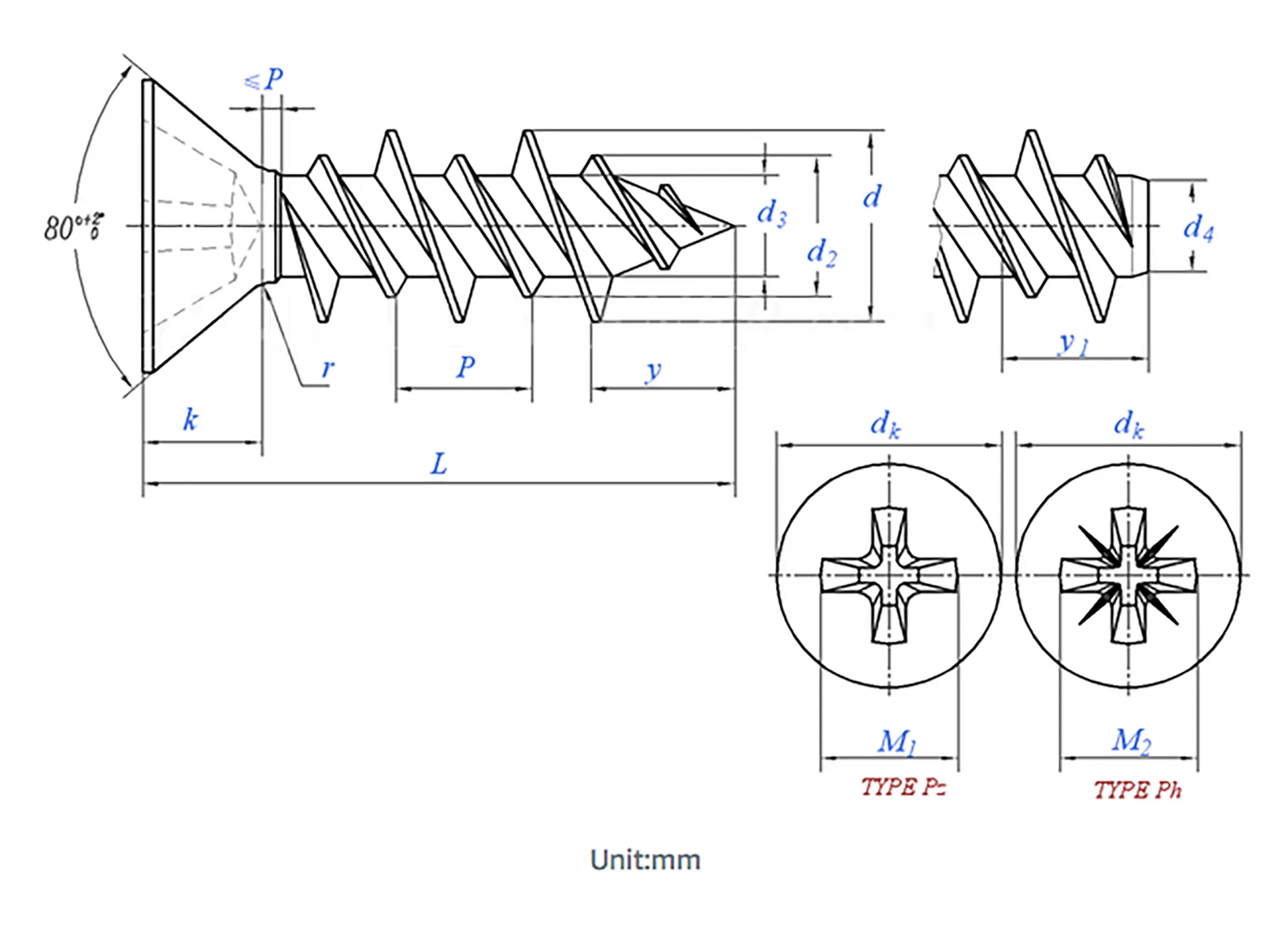
Parameter
 x
x