TEL:+86 15630072814
Stainless Steel Long Nuts |304 & 201 Material | Bulk Supplier of Long Nuts | Competitive Price
home >
Products >Stainless Steel Fastener >Long Round Nut > Stainless Steel Long Nuts |304 & 201 Material | Bulk Supplier of Long Nuts | Competitive Price
Stainless Steel Long Nuts |304 & 201 Material | Bulk Supplier of Long Nuts | Competitive Price
DESCRIPTION
PRODUCT Tags
Stainless Steel Round Elongated Nut Selection Guide
201 Stainless Steel:
Advantages: Lower cost with certain corrosion resistance.
Disadvantages: Higher manganese content makes it prone to rust in humid, high-salinity (e.g., coastal areas), or chemically corrosive environments.
Applicable Scenarios: Cost-sensitive applications, dry indoor environments, and general structural connections with low corrosion resistance requirements.
Advantages: Lower cost with certain corrosion resistance.
Disadvantages: Higher manganese content makes it prone to rust in humid, high-salinity (e.g., coastal areas), or chemically corrosive environments.
Applicable Scenarios: Cost-sensitive applications, dry indoor environments, and general structural connections with low corrosion resistance requirements.
304 Stainless Steel:
Advantages: Recognized as a universal stainless steel, it contains higher nickel and chromium content, offering excellent corrosion resistance, rust resistance, and better machinability and toughness.
Disadvantages: Higher cost compared to 201 stainless steel.
Applicable Scenarios: Outdoor construction, coastal facilities, food machinery, chemical equipment, medical devices, and other applications requiring high hygiene and corrosion resistance. For most industrial applications, 304 stainless steel is recommended.
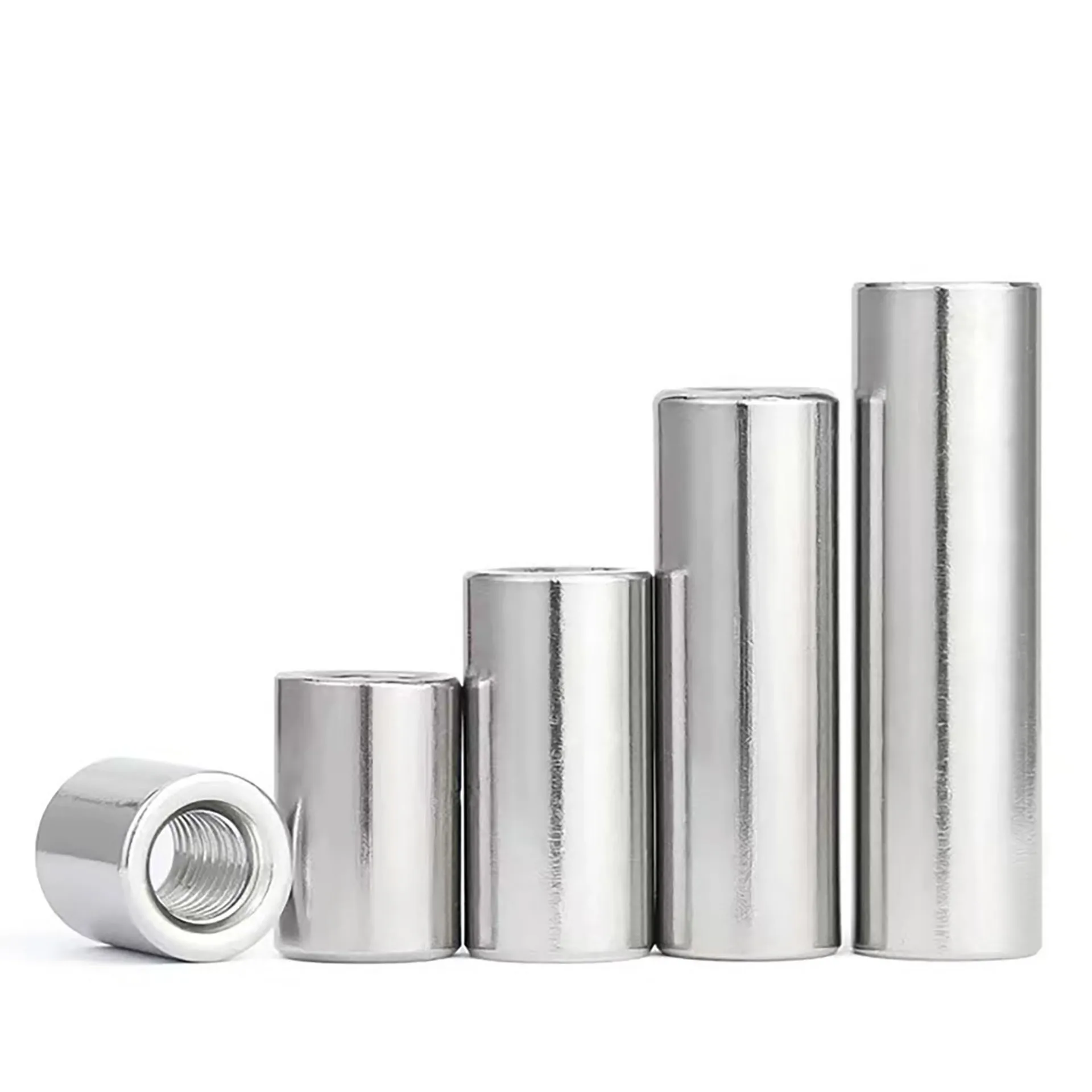
Specifications & Dimensions
Thread Specification:
Metric: e.g., M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, M20, etc. This is the most commonly used standard domestically and must exactly match the diameter and pitch of the bolt.
Imperial: e.g., 1/4"-20, 3/8"-16, 1/2"-13, etc. Primarily used for imported equipment or specific fields.
Nut Length:
The length (L) of an elongated nut is its core feature, typically 2-4 times or even longer than that of a standard nut.
The length selection depends on the required increase in thread engagement length. Generally, longer engagement length enhances connection strength and anti-loosing. The specific length should be determined based on design requirements.